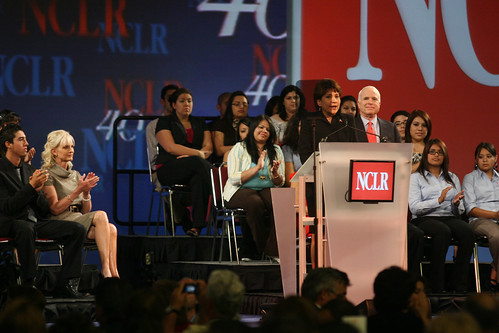(Attn. Homeland Security: In photography, “shooting” is a term we use for “photographing” someone. You know, as in “photo shoot.” So no need to worry. And by “worry”, I mean wiretap, surveil, or put me on a list. I’m not a terrorist.)
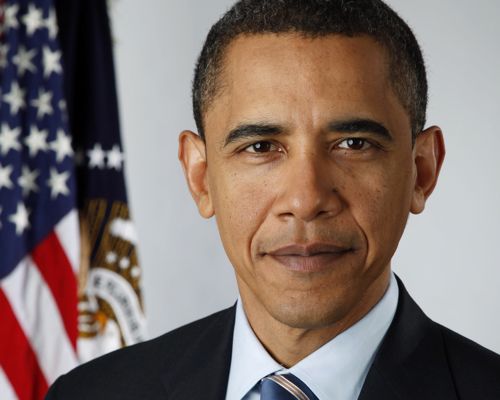
In July, I was fortunate enough to get the photo assignment to shoot presumptive presidential nominees John McCain and Barack Obama. They visited San Diego for the National Council of La Raza conference.
Barack Obama at the National Center of La Raza Conference

Obama delivered a speech punctuated by applause. But it was still a bit lukewarm compared to what I expected. I’d heard stories of his charismatic delivery and rockstar-like receptions. That was all there, I guess, but there was a lingering stress in the air. Obama needed to get defeated Hillary Clinton supporters excited about voting for him. He got loud cheers in reference to oppressive immigration raids, but applause was absent from his discussion of details: securing the border first, path to citizenship starts at the back of the line, fines for non-legal status, etc. When the speech was over, he shook hands with the students seated behind him and made his way slowly through the front edge of the crowd.
The press were given a sideline area at about half-court in the convention center’s large ballroom. My 70-200mm zoom lens only got me close enough for a decent medium-wide shot. I had to crop the shot above by 50 percent to get something usable. At this distance, my lens looked pretty weak compared to the pros bumping shoulders next to me — the ones you see at sports games with what look like space-age sniper rifles. I was disappointed that I wasn’t able to get closer and, more specifically, that we weren’t allowed to get any closer. The only concession was being taken two-by-two into the center aisle for about 60 seconds, once.
John McCain at the National Council of La Raza Conference
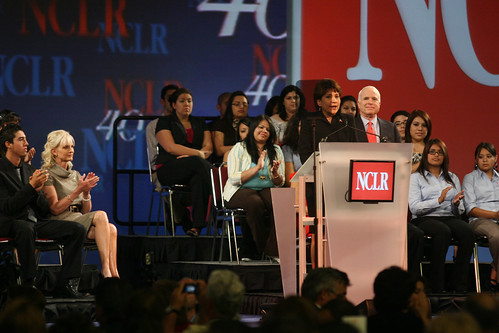
McCain’s appearance had a dramatically different tone. For starters, his wife Cindy McCain accompanied him on stage. It felt warmer than Obama’s solo performance, somehow less formal and more classy at the same time. I couldn’t help thinking McCain scored a few extra “family values” points with the Latino crowd. He spoke not as if he were trying to impress, but as if he were having a conversation with friends. He took questions from the audience after his speech. And after conference organizers said the Q&A session was over, McCain threw the microphone into the crowd to take another question.
Before the speech began, there were rumors that we’d be escorted in small groups to the front lines. Apparently the McCain people caught wind of photographer’s complaints and agreed to allow us better access than during Obama’s speech. The conference staff members I spoke with said the campaign staff set the rules in terms of press access, not the conference itself.
Conclusions
McCain’s performance was definitely the most interesting of the two candidates, not only in terms of his interaction with the crowd but in his campaign’s interaction with the press. But I’m not sure how much of a difference it makes in the end. Of the photos I uploaded to Flickr, Obama’s mediocre shots have been viewed more than twice as much as McCain’s more dynamic photos. And of McCain’s, two-thirds of his views come from the photos of his wife Cindy.
We don’t learn anything terribly valuable from these numbers. Yeah, Obama has more buzz than McCain. And on average, Cindy McCain has more than either of them. Perhaps it’s really only an indicator of the superficial nature of the statistical mob. We can only hope the people vote based on their version of who will be the best president, not merely on who will be a best looking one.